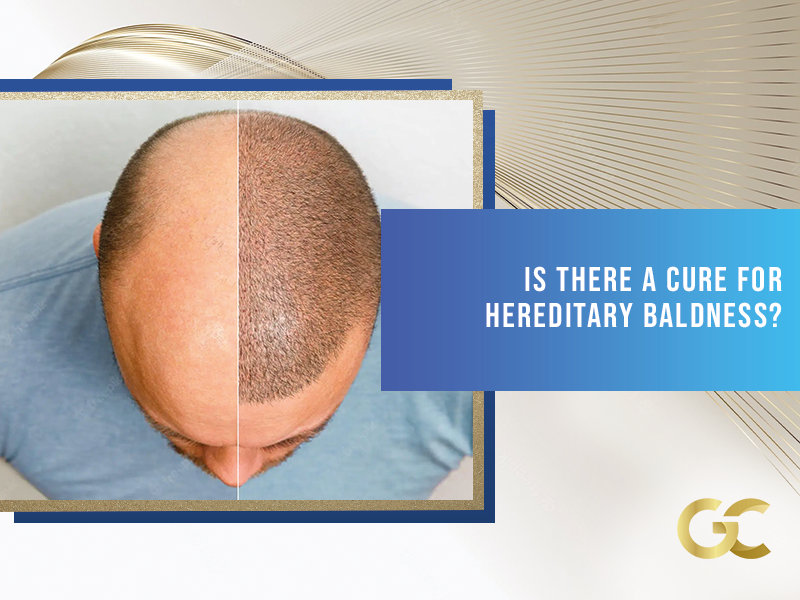
People suffering from androgenetic alopecia often ask any doctor if there is a cure for hereditary baldness. If they knew the mechanisms behind the process of hair loss, they would know the answer already.
Why Does Hereditary Baldness Happen?
Hereditary baldness, as the name indicates, is a hereditary condition, inherited from one or both parents via genes. The genes that cause this condition make you more sensitive to the effects of the hormone dihydrotestosterone (DHT), even in small quantities.
DHT is a by-product of testosterone, which is the main male sex hormone. Its production happens when an enzyme called “alpha 5 reductase” converts free testosterone into DHT.
What DHT does is that it binds itself to the hormonal receptors located in your hair follicles, reacting with them. The reaction ultimately makes the hair follicles start shirking progressively until a point that they will grow no longer.
This is the actual reason behind baldness. DHT is the cause, and therefore, some treatments focus on it and prevent it from reaching your hair follicles.
Does a Cure for Hereditary Baldness Exist?
No, there is no cure. The condition is genetic—meaning that if you have the bad genes active within you, it is going to happen. Any product which claims to be the definitive cure for baldness, either stopping it or regrowing the hair, is likely a misdirection.
There are many such products available, some of them rather costly, that play with the hopes of the consumers and yet underdeliver. That said, there are also a few treatments that can do something to improve your hair loss due to androgenetic alopecia. Here are some of them.
Minoxidil
Commonly known as Rogaine due to the popularity of a product that contains it. It’s a topical solution available over the counter and, thus, without the need of any prescription. It stimulates hair growth by supplying nutrients to the hair follicle and facilitating blood circulation to the zone.
Results are visible after six months of continuous treatment, applying it two times a day. It comes in both liquid and foam forms; both of which have the same effect.
It is also available at 5% and 2% concentration, being 2% recommended for women. Note that minoxidil only grows hair but does not treat hair loss causes.
Finasteride
Also known as Propecia. It was a prescription drug for treating men with enlarged prostates until the discovery of its hair loss-stopping effects. It works as an alpha 5 reductase inhibitor, disrupting the capacity of the said enzyme to produce DHT.
Thus, it prevents your hair follicles from shrinking. Some side effects might occur though, like diminishing sex drive among them. The drug is only for men. Women would risk severe negative effects, and pregnant women should not even touch these pills.
Hair Transplant as a Cure for Hereditary Baldness
An FUE hair transplant does not “cure” hereditary baldness in a sense it makes your shrunk hair follicles grow again. Rather, it provides “new” hair follicles to the balding area that will grow there.
By making an incision with a scalpel that is 1 mm or less in diameter, our surgeon extracts hair follicles from the back of the scalp one by one. Once he has all he needs, he will proceed to graft them into the balding area through microincisions. The hair follicle will take to the receiving site and start to grow normally.
Hair transplants, compared to the medications, is the most effective way to fight against hair loss. Without any side effect and hard process, you can regain your healthy hair within a few months.
Our surgeons perform high-quality hair transplants at affordable prices. Contact us if you are looking for a permanent solution to your hereditary baldness problem.