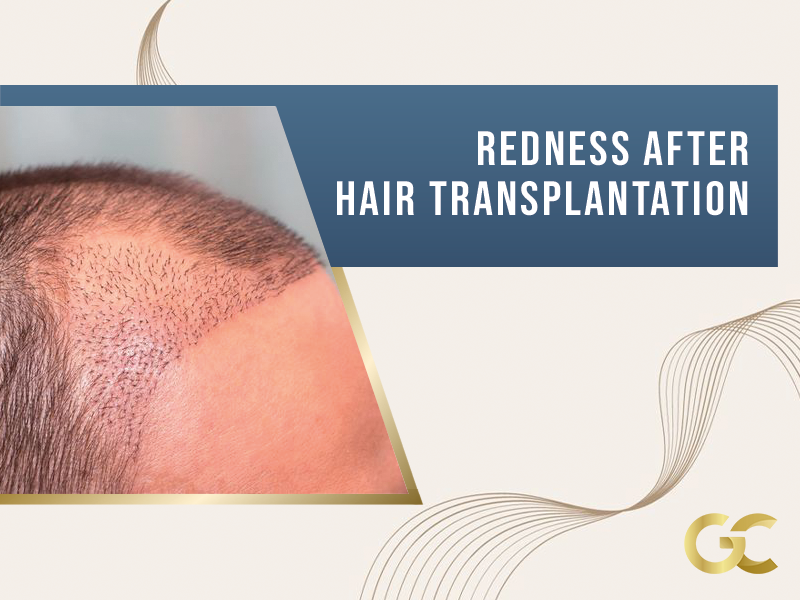
is a concern of many people who want to have a hair transplant. So what is the cause of this rash look? In fact, this situation is quite natural and occurs depending on the healing process of the scalp after transplantation. It is completely temporary to experience redness after hair transplant surgery. It may take anywhere from one to four weeks to disappear. Unfortunately, th
is period may be longer in patients with lighter skin color. It may take longer for the red image on the skin to disappear.
The hair transplantation process involves the extraction of the follicular units of your hair (along with the hair follicles of your hair strands) one by one from the donor area. The surgeon makes a small, circular incision around the hair follicles with the help of a microneedle. Hair follicles are then pulled out, leaving a small hole in the skin. Each follicle unit contains one to four strands of hair. These follicular units are called grafts. The grafts are then transplanted to the balding areas of your head where they will grow into healthy hair follicles.
There May be Swelling After Hair Transplantation
After hair transplantation, there may be some redness and swelling on the tissues on each transplanted graft, around the crusts, or crusts. These scabs, which are completely natural and an indicator of healing, and redness after hair transplantation will disappear in a short time if appropriate washing and other preventive instructions given by the surgeon will disappear after a period of five to eight days.
After FUE hair transplantation redness is inevitable beyond being common. It is not possible to be permanent under normal conditions. However, in some extreme cases, you may need treatment for the removal of the redness and for a full recovery.
In Which Areas Does Redness Occur?
These rashes that begin to be seen immediately after hair transplantation are seen on the back of your head and where the hair was transplanted. The operation involves making small incisions on your skin. Taking a donor’s hair and transplanting it to the desired location by making small incisions means opening many tiny wounds, although the risk of complications in the scalp is very low.
How Long Does The Redness Last?
After hair transplantation, redness completely disappears after 2 weeks in many patients. As your scalp starts to heal, the redness begins to decrease rapidly. Although most hair transplants heal completely within 10-14 days, this healing process may take longer in some large hair transplantation cases. As a result, it may take up to a month for the rash to resolve completely.
Does Redness Affect Hair Transplantation?
Normal healing redness should not affect your hair transplant. However, in some cases, the rash does not cause normal improvement. You need to see your doctor check your recovery. Redness after hair transplantation may have reasons that do not occur due to healing. Some of these reasons are;
Folliculitis
Some patients may suffer from infection around newly transplanted hair follicles. The most important symptom of this infection called folliculitis is redness after hair transplantation. The risk of this infection occurring can take up to 8 months. Folliculitis looks like small pimples. And it is clustered between the hair strands. It may feel warm, itchy, and painful. The cause may be a bacterial infection, but in most cases, bacteria are not found.
Treatment of folliculitis is often effortless and simple. Your physician may even choose not to apply any treatment for this condition. In this case, it will gradually heal on its own and the redness will end after hair transplantation. However, this decision should definitely be made by your physician. Your doctor may suggest that you use warm compresses or a range of antibiotic / antibiotic creams to help fight any bacteria that may be there. You need to make sure you keep your scalp as hygienic as possible to prevent further infection problems.
Cellulite
Cellulite includes a skin infection on your scalp. After hair transplantation, your skin is at risk of bacteria entering and causing infection. If you have cellulite, you may notice your redness spreading, your scalp sore, and even a fever. If you have these symptoms, it is important to see your surgeon immediately. A series of antibiotics and daily follow-up may be required to make sure your infection is healing. During the recovery period, the spread of the redness slows down, stops and eventually, the redness disappears after hair transplantation.
Cysts
Cysts are small round sacs that grow under the skin. It can occur in your donor or recipient area. There are a number of potential reasons, such as not removing grafts from the donor area or not properly transplanting. Cysts can also be caused by your skin healing abnormally. Symptoms of cysts are swelling, redness, and pain.
If you suspect the formation of a cyst, you should start the treatment by contacting your surgeon immediately. Your surgeon may decide to remove the cyst for treatment or recommend using a warm compress on the area.
Skin Necrosis
Skin necrosis is a condition in which your skin is dead or dying. Its incidence is not high after hair transplantation. It looks like a deep crust on your skin and can appear on the back of your head or wear the hair was transplanted. It may occur within the first 2-4 weeks after surgery. You may notice that your skin starts to appear dark or purple in color. As soon as it is noticed, you should get support from the nearest health institution or your doctor.
What Are The Rules After Hair Transplantation?
- Do not shower under very hot water.
- Avoid smoking and drinking alcohol for at least two weeks after the hair transplant.
- Use medical products as recommended by the hair transplant center.
- Cover your head with a bandana or hat to avoid direct contact with harmful UV rays.
- Do not touch the areas where hair follicles are transplanted. Also, avoid scratching and rubbing your hair with your nails.
- Sleep in a semi-sitting position.