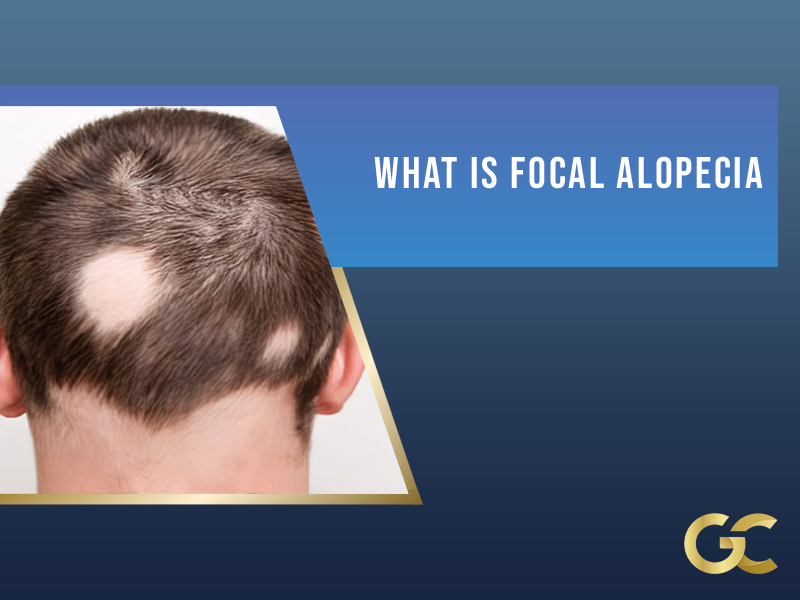
Focal alopecia or nesting alopecia is one of the many hair loss-causing conditions. The principal characteristic of focal alopecia is a sudden loss of hair on the scalp in circular spots.
Balding spots resemble the shape of a coin and are usually accompanied by inflammation of the zone.
Cause of Focal Alopecia
The falling of the hair is due to an autoimmune disorder that leads your body to believe that it is under attack falsely. Immunological systems start to deal with the disease, but since there isn’t one, it’ll attack your cells, including follicles.
Resulting hair loss from it is merely aesthetical, but many people find it concerning and get upset because of the alteration of their looks.
Women are more prone to extreme emotional responses ranging from anxiety and depression to psychotic bouts. Men don’t fare well either. However, they are more likely to embrace baldness if there’s no choice.
Who Suffers from Focal Alopecia?
People at risk of developing focal alopecia present one or many of these characteristics:
- Have a family history of baldness (hereditary alopecia)
- Are prone to chronic illness
- Were victims of viral infections
- Are suffering from severe psychological stress or depression
- Suffer from endocrine disorders such as thyroid disease
- Have nervous system-related disorders
The rate of hair loss can increase dramatically if two or more of those characteristics overlap.
Treatments for Focal Alopecia
For treating cases of focal alopecia, the use of the following substances is often recommended:
- Minoxidil: Aids the growth of new hair in the applied zone. It is available over the counter in liquid and foam presentations. Minoxidil helps to grow the hair back, but it does not treat the underlying causes.
- Dihydrotestosterone blockers or antiandrogens: DHT is the hormone responsible for hormonal hair loss. It spawns from testosterone via conversion through an enzyme. Hormonal blockers for DHT or antiandrogens can prevent said conversion and potentially stop the hair loss. Be mindful that said blockers and antiandrogens have several side effects, consult a doctor before taking them.
- Anti-inflammatories: They can help manage the follicle’s inflammation; in a few cases, this is enough to stop the hair loss for a time. The underlying causes must be promptly dealt with in order to prevent the return of chronic symptoms.
- Immunosuppressants: They are commonly used to reduce the body’s immune responses to perceived threats. It can reduce the immunological response that caused the fall of the hair follicles for a time.
Until the healing of the underlying causes, chronic symptoms will recur, and therefore, the treatment shall continue.
Hair Transplant to Treat Focal Alopecia
In the case of either a spot or most of the top of the scalp has run out of healthy follicles, a hair transplant is still a viable choice.
During the procedure, the surgeon excises healthy follicles from the base of the scalp. Those are then grafted in the balding spot via incisions on the scalp and left to grow.
Modern techniques allow natural-looking results that will grow seamlessly in the right direction. Hair transplant surgeries to treat hair loss is an option for both men and women.